In the previous two articles of this Ansible series, we explained how to install and configure Ansible to run commands and perform complex tasks in several remote servers simultaneously.
In the current tutorial we will explain how to set up WordPress in the same remote servers:
node1: 192.168.0.29 node2: 192.168.0.30
where we installed, enabled, and started Apache (you probably know by now why we chose to work with a web server as an initial example in the last tutorial).
I highly encourage you to read Part 1 and Part 2 before proceeding further in order to make sure you’re familiar with the concepts associated with Ansible.
How to Install and Configure ‘Ansible’ Automation Tool for IT Management – Part 1
How to Use Anisble Playbooks to Automate Complex Tasks on Multiple Remote Servers – Part 2
Step 1: Introducing Ansible Roles
As you start adding more and more tasks to plays, your Playbooks can become increasingly difficult to handle. For that reason, the recommended approach in those situations (actually, in all cases) is to use a directory structure that contains the directives for each group of tasks in distinct files.
This approach allows us to re-use these configuration files in separate projects further down the road. Each of these files define what is called in the Ansible ecosystem a role.
In our case, we will create two roles. One of them (called wp-dependencies) will be used to install the WordPress dependencies (PHP and MariaDB – no need to install Apache as it’s already installed).
The other role (named wp-install-config) will include all the necessary tasks associated with the installation and configuration of WordPress.
Step 2: Creating Ansible Roles
Ansible comes with an utility called ansible-galaxy that will help us to create the directory structure for our roles. We will do this in /etc/ansible/playbooks (which we created in Part 2) but in theory you can set it up in another directory if you want.
# cd /etc/ansible/playbooks # ansible-galaxy init wp-dependencies # ansible-galaxy init wp-install-config
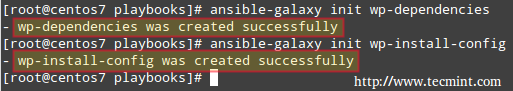
Next confirms the newly created roles.
# ls -R /etc/ansible/playbooks
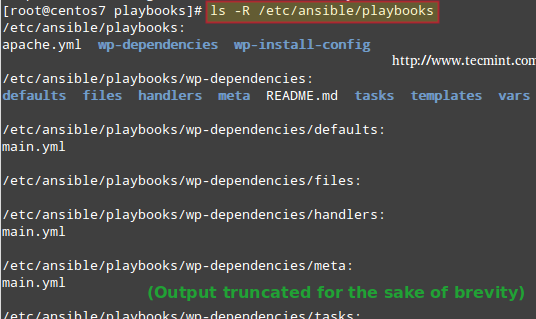
In the above image we can see that ansible-galaxy created two directories with the same name as our roles, and other subdirectories (defaults, files, handlers, meta, tasks, templates, and vars) and a README.md file inside each of them.
In addition, a YAML file named main.yml was created inside all of the directories listed earlier, with the exception of files and templates.
We will begin by editing the following configuration files as indicated:
1. /etc/ansible/playbooks/wp-dependencies/tasks/main.yml. Note that we are including httpd in case you have not followed along with the previous tutorials of this series.
---
# tasks file for wp-dependencies
- name: Update packages (this is equivalent to yum update -y)
yum: name=* state=latest
- name: Install dependencies for WordPress
yum: name={{ item }} state=present
with_items:
- httpd
- mariadb-server
- mariadb
- php
- php-mysql
- MySQL-python
- name: Ensure MariaDB is running (and enable it at boot)
service: name=mariadb state=started enabled=yes
- name: Copy ~/.my.cnf to nodes
copy: src=/root/.my.cnf dest=/root/.my.cnf
- name: Create MariaDB database
mysql_db: name={{ wp_mysql_db }} state=present
- name: Create MariaDB username and password
mysql_user:
login_user=root
login_password=YourMariaDBRootPasswordHere
name={{ wp_mysql_user }}
password={{ wp_mysql_password }}
priv=*.*:ALL
2. /etc/ansible/playbooks/wp-dependencies/defaults/main.yml
--- # defaults file for wp-dependencies wp_mysql_db: MyWP wp_mysql_user: wpUser wp_mysql_password: wpP4ss
3. /etc/ansible/playbooks/wp-install-config/tasks/main.yml:
--- # tasks file for wp-install-config - name: Create directory to download WordPress command: mkdir -p /opt/source/wordpress - name: Download WordPress get_url: url=https://www.wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz dest=/opt/source/wordpress/wordpress.tar.gz validate_certs=no - name: Extract WordPress command: "tar xzf /opt/source/wordpress/wordpress.tar.gz -C /var/www/html --strip-components 1" - name: Send config file copy: src=/root/wp-config-sample.php dest=/var/www/html/wp-config.php mode=0644
4. wp-config-sample.php (provided in this Pastebin) as follows and save it to your Ansible controller machine (as you can see in the last copy directive above, I downloaded it to the home directory of the superuser (/root/wp-config-sample.php).
Important: Please note that the value for variables DB_NAME, DB_USER, and DB_PASSWORD are the same as in /etc/ansible/playbooks/wp-dependencies/defaults/main.yml:
…
/** The name of the database for WordPress */
define('DB_NAME', 'MyWP');
/** MySQL database username */
define('DB_USER', 'wpUser');
/** MySQL database password */
define('DB_PASSWORD', 'wpP4ss');
…
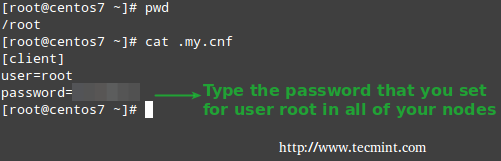
5. For new database server installations where the root password is empty, such as in this case, unfortunately we need to setup the password for user root individually in every machine through mysql_secure_installation.
As far as I know, there is no available workaround that will allow you to set up the root password via Ansible in the same step where you create the administrative database account for WordPress.
Make sure you use the same password in all hosts, then copy the credentials in /root/.my.cnf (the actual location may differ in your case, but in all instances it needs to match the value of the src parameter for the task Copy ~/.my.cnf to nodes in /etc/ansible/playbooks/wp-dependencies/tasks/main.yml).
In that file (see above) we’ve assumed that the password for root is YourMariaDBRootPassword.
6. Next, our playbook (/etc/ansible/playbooks/playbook.yml) will look much more organized and simple when compared to the previous tutorial:
# cat playbook.yml
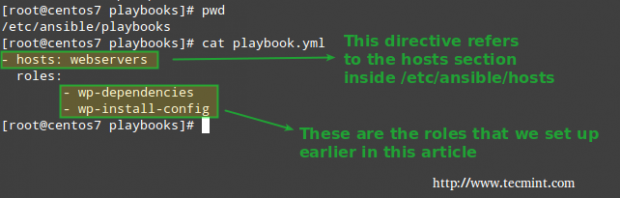
- hosts: webservers
roles:
- wp-dependencies
- wp-install-config
Finally, it’s time to run these tasks by invoking our playbook:
# ansible-playbook playbook.yml
Now let’s check if we can access the WordPress Admin page using the IP addresses of node1 192.168.0.29 and node2 192.168.0.30:

You can view the last two steps in the following screencast:
As you can see, you can set up multiple WordPress installations with little to no effort using Ansible. Then you can use the respective Admin user interface to configure each site separately.
Final considerations
If you are using another distribution to deploy WordPress, the packages name may vary, but it comes down to installing the Apache web server, the MariaDB database server, and the Python MySQL module. If that is the case, use your distribution’s software management system to search for the exact package name that you need to install.
Summary
In this series we have explained how to use Ansible to run commands and execute complex tasks in several Linux machines simultaneously.
One of such examples is setting up WordPress, as we have discussed in this guide. Whether you are a system administrator or a blogger, I hope you have found the concepts and examples in this tutorial useful.
Best of luck and do not hesitate to drop us a line if you need help or have any comments or suggestions!



Hi, I am getting this error:
fatal: [172.31.26.76]: FAILED! => {“changed”: false, “msg”: “unable to connect to database, check login_user and login_password are correct or /root/.my.cnf has the credentials. Exception message: (1045, \”Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: YES)\”)”}
fatal: [172.31.20.203]: FAILED! => {“changed”: false, “msg”: “unable to connect to database, check login_user and login_password are correct or /root/.my.cnf has the credentials. Exception message: (1045, \”Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: YES)\”)”}
Where is the 4th part from the Ansible series
@Khawaja,
The part 4 Ansible series is in progress, we will publish soon, till then stay tuned to Tecmint.com.
It is possible to set root password (mysql_secure_installation). I’ve created my own playbook and i am able to do the all configuration.
I have set root password, removed anonymous user, remove test database from Ansible.
Please check again and mention these steps also in this article.
Hi I am getting this error:
TASK: [wp-dependencies | Create MysqlDB database] *****************************
failed: [192.168.1.237] => {“failed”: true}
msg: the python mysqldb module is required
FATAL: all hosts have already failed — aborting
I have already installed MySQL-python.x86_64 0:1.2.3-11.el7 on ansible server. Can you please help?